5. Using New Security and Safety Features of IE8
The new security and safety
features of Windows Internet Explorer 8 are designed to help protect end
users from malicious attacks or attempts to get personal information
from the user without their knowledge. Users expect things to be as they
appear which is not always the case. Because we all use the internet
and our corporate intranets to provide information every day, online
crime has risen dramatically.
The new type of criminal we
face are known as cybercriminals, and they are using extremely
deceptive and sophisticated methods for getting information from end
users. One method is the use of malware to steal private information
through software pretending to be an expected website. This malware
could be a program running on your PC which reads everything you type
(including login information from a web browser) and reports the info
back to a cybercriminal. Phishing is another technique used by
cybercriminals to gain personal information from users. Phishing can be
perpetrated by the cybercriminal pretending to be a legitimate website
such as the user's banking site or credit card site and getting the end
user to enter information into a fraudulent page.
New features of IE8 helping
to identify malware and phishing schemes will make it easier for end
users to quickly identify potential issues and allow the administrators
to spend less time "fixing" the network and user-compromised data.
Domain Highlighting, Cross Site Scripting Kilter, Click-Jacking
prevention, Smart Screen filters, a -InPrivite Browsing, and InPrivate
Filtering are new additions to Windows Internet Explorer 8.
5.1. Using Domain Highlighting
Domain Highlighting is one
of the new features in Windows Internet Explorer 8 that gives the user
more feedback about the website they are visiting. When a user surfs to a
website, they normally type in a Uniform Resource Locater (URL) in the
form of, for example, www.bing.com.
This is displayed in the address bar of the browser, and the user can
see it during the entire browsing session. This may or may not be
apparent to the user as it is in nondescript text and nothing jumps out
at them. In IE8, the displayed URL is shown to the user with the domain
highlighted, for example, www.bing.com. As the user continues to surf to other pages within Bing, the domain portion, bing.com,
remains clear (the other text softens to gray) so if the user is
redirected to another site, there is a visual clue jumping out at the
user.
If you take a look at Figure 8, you can see the same search string issued in both Windows IE7 and IE8. Notice how much better bing.com stands out in the Windows Internet Explorer 8 address bar.

Domain Highlighting and
user education are a good starting place for security and safety, but
are there features that can be added to proactively help the user? Yes,
one of the more common phishing/malware activities is Cross Site
Scripting (XSS), where the user inadvertently runs a script in a website
link exploiting a flaw in the website, or Click jacking, where a user
clicks a link that says one thing on the page but sends the user
somewhere else. IE8 has proactive software to help identify these types
of phishing/malware attacks before they can happen.
5.2. Defending Against Cross-Site Scripting and Click-Jacking
Cross-site
scripting (XSS) attacks attempt to exploit vulnerabilities that exist in
the websites you use. XSS attacks are set up by inserting an address to
a malicious website in a link a user might click on in an email. The
data in the link directs the browser to a legitimate website that has
been compromised to contain malicious code that can capture keystrokes,
letting the cybercriminal capture a user's login credentials (user name
and password).
As a leading
compromise today, Windows Internet Explorer 8 includes a Cross Site
Scripting filter that attempts to detect these types of attacks and
disable the harmful scripts. If users surf to a website that has been
compromised, the problem can be detected and 1E8 can modify the request,
avoiding the potential risk.
A message will appear
at the top of IE8 page indicating to the user that "Internet Explorer
has modified this page to help prevent cross-site scripting." Figure 9
shows the message displayed when a malformed query is issued to a
search engine. The user can click the message to get further information
about the compromise.

As with all of technology
and cybercrime, it's a cat-and-mouse game between the administrators
and users, and the cybercriminals. Every time the good guys find a way
to block or mitigate an attack, the bad guys (good or bad I guess
depends on your point of view) find a different way to perpetrate an
exploit. Click-jacking is a growing threat to our online community. A
savvy cybercriminal can create a website where a real page is placed in a
frame in the attacker's page.
Clicking on an item in the
attacker's page allows the attacker to manipulate your input and have
you view an advertisement at best or change your browser parameters at
worst. Windows Internet Explorer 8 includes code that will allow
developers to prevent their websites from getting inserted into a frame
in the IE8 interface, helping to mitigate the click-jacking problem.
The cross-site
scripting filter and click-jack prevention code offer protection against
malicious code in a website. There is also a set of tools included in
Windows Internet Explorer 8 that help prevent the user from visiting a
website that has been reported as unsafe or downloading content that has
been reported as unsafe. This protection is known as Smart Screen
filtering.
6. Working with SmartScreen Filters
Microsoft maintains
a database of unsafe websites that is checked while a user is browsing
through websites. If an unsafe website is chosen, IE8 wilt block the
user's request and present a page displaying the fact that the page has
been identified as unsafe and changing the background color of the
address bar to reflect the same.
The user can continue to
the web page if they are confident of the safety of the website by
choosing More Options and continuing to the website. This functionality
is part of the IE8 suite of technologies helping to protect the users
from the deceptive practices of cybercriminals. The SmartScreen filters
also have the ability to block malware or phishing from within initially
safe sites by including specific pages identified as unsafe in the
Microsoft unsafe website database.
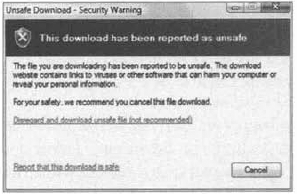
Another new feature added to
SmartScreen filters is the ability to protect the user from unsafe
downloads. If a user attempts to download a file and the file has been
reported as unsafe (and accepted into the Microsoft database as unsafe),
an Unsafe Download security warning dialog box is generated and the
user is prevented from downloading the file. As with the unsafe website
filters, the user can still choose to continue the download if they are
confident the file they are requesting is safe, as shown in Figure 10.
Administrators do have the
option of configuring Group Policy for Windows Internet Explorer 8 to
disable the ability of the users to download unsafe files if this is
desired. You do have the ability to manage Smart Screen Filtering
functionality from the Safety menu of IE8. Figure 11
shows the option to select Turn Off Smart Screen Filter.... From the
Smart Screen filter menu choice you do have the ability to check whether
the current site has been reported as unsafe (let's say you turned off
Smart Screen Filtering but would like to check a specific site).
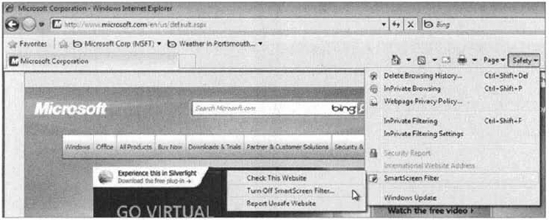
The Smart Screen Filter menu
option also gives you the ability to report a website as unsafe. Once
submitted, Microsoft will review the site and add it to their database
if they determine it meets the criteria they have put in place for an
unsafe website. Microsoft has also added two new features to protect a
user's personal information. The new features are InPrivate Browsing and
InPrivate Filtering.
6.1. Using InPrivate Browsing and InPrivate Filtering
InPrivate browsing provides
some level of privacy to users using Windows Internet Explorer 8. The
privacy maintained with InPrivate browsing relates to current browsing
where an InPrivate session has been enabled. The InPrivate session
prevents the browsing history from being recorded nor will temporary
internet files be retained. Cookies, usernames, passwords, and form data
will not remain in IE8 following the closing of the InPrivate session
nor will there be any footprints or data pertaining to the InPrivate
browsing session.
This is a good method of
protecting user data if you are not surfing from your own machine or are
surfing from a public location (always a bad place to leave personal
information). InPrivate browsing can also be used if you don't want
anyone to be able to see data from your internet browsing session.
There are several ways to
launch an InPrivate IE8 browsing session. One way is to open a new tab
and select the Open An InPrivate Browsing Window option from the Browse
With InPrivate section. This will open a new tab and the tab will be an
InPrivate session. You can also choose to open Windows Internet Explorer
8 and start an InPrivate session directly by choosing the Safety menu
item and selecting the InPrivate Browsing menu choice.
You can also open a new IE8 browser and press Control+Shift+P. Figure 12 shows an InPrivate session launched with Control+Shift+P and going to login.live.com. This will ensure any of my login and browsing information will not be saved to this computer.
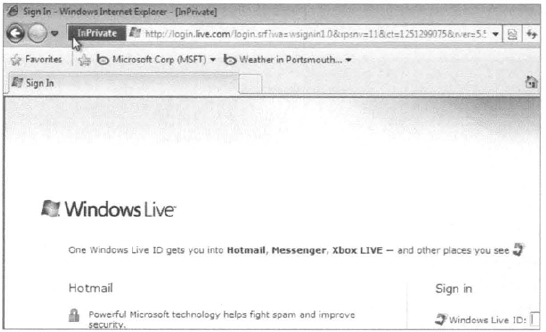
InPrivate Browsing keeps
information from being saved to the local machine while the session is
active, but don't get lulled into a false sense of security; malware,
phishing, and other methods that send data out of the local machine are
still valid and can provide personal information to a cybercriminal.
InPrivate Filtering
takes a slightly different approach in providing security and safety to
the user who is surfing using Windows Internet Explorer 8. Many of
today's websites gather content from different sources as they present a
web page to you. Some of these sources are websites outside the main
location, and they provide third-party companies with tracking
information about where you surf and what you look at.
This information can then
be used to provide statistics as well as send advertisements back to
you. InPrivate Filtering provides an added layer of control for the user
to decide what information third-patty websites will have access to
while the user is browsing, limiting the ability of third-party websites
to track their browsing usage.
InPrivate Filtering is not
enabled by default and must be enabled per browsing session. It is
enabled from the Safety menu in IE8. You can alternatively use
Control+Shift+F to enable InPrivate Filtering.
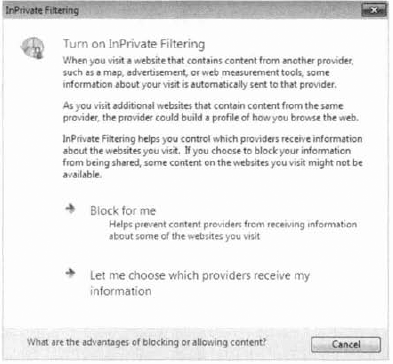
Once you choose
InPrivate Filtering, you will be given the option to have IE8
automatically block some third-party content or choose to let the user
select which third-patty providers will receive the user's browsing
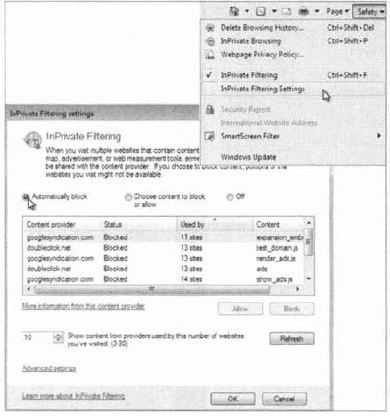
information (Figure 13). You can always go back and change the options later or turn off InPrivate Filtering if you desire.
After InPrivate Filtering
is enabled, you can see which pages have been blocked as third-party
queries from the InPrivate Filtering Settings dialog box. The InPrivate
Filtering Settings dialog is an alternate location for enabling
InPrivate Filtering (as shown in Figure 14) or disabling it. You open InPrivate Filtering Settings from the Safety menu item of Windows Internet Explorer 8.
Along with the new
security and safety features of Windows Internet Explorer 8, there are
several enhancements to existing features. Some of the enhanced items
include Data Execution Prevention, Automatic Crash Recovery, and
Enhanced Delete Browsing History.
One of the many
advantages of IE8 is that you can configure the web content filter. IE8
also allows you to set up and configure the Allow and Block lists. The
Allow and Block lists are lists that you can subscribe to that will
automatically filter out certain websites.